What is Series Parallel Circuit? Formula, Diagram, Calculator
Introduction:
Series-parallel circuits are a combination of both series and parallel circuit configurations. They are commonly found in electrical and electronic systems, and understanding their properties and calculations is crucial for engineers and technicians. In this article, we will explore what series-parallel circuits are, discuss the formulas, provide examples, explain the laws governing them, highlight the differences between series and parallel circuits, and conclude with a brief overview of calculating transistors in series or parallel.
What is a Series-Parallel Circuit?
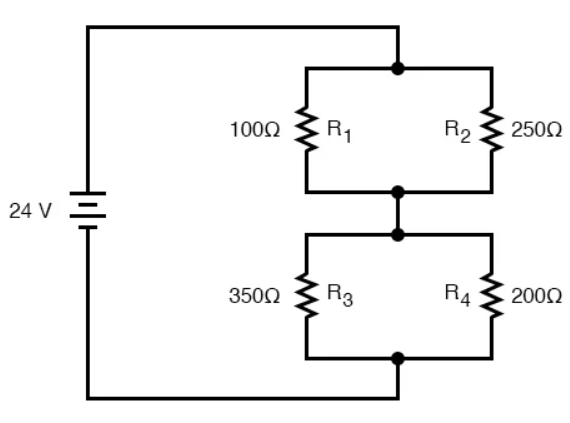
A series-parallel circuit is a circuit arrangement where components are connected both in series and parallel. It combines the characteristics of series circuits, where components are connected in a single path, and parallel circuits, where components are connected in multiple paths. This configuration allows for more complex and versatile circuit designs.
Series-Parallel Circuit Formula:
Calculating the total resistance (RT) in a series-parallel circuit requires applying a combination of series and parallel formulas. For resistors connected in series, the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances: RT = R1 + R2 + R3 + ... For resistors connected in parallel, the reciprocal of the total resistance is the sum of the reciprocals of individual resistances: 1/RT = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 + ...
Series-Parallel Circuit Examples:
Let's consider an example of a series-parallel circuit. Suppose we have three resistors: R1 = 10 ohms, R2 = 20 ohms, and R3 = 30 ohms. If R1 and R2 are in series and connected in parallel with R3, we can calculate the total resistance as follows:
RT = R1 + R2 // R3
= (10 + 20) // 30
= 30 // 30
= 1 ohm
In this example, the total resistance of the series-parallel circuit is 1 ohm.
Series-Parallel Circuit Laws:
The laws governing series-parallel circuits include Ohm's Law, Kirchhoff's Laws, and the Voltage and Current Division Laws. Ohm's Law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across it and inversely proportional to its resistance. Kirchhoff's Laws deal with the conservation of charge and energy in electrical circuits, while the Voltage and Current Division Laws determine how voltages and currents divide in series and parallel branches.
Series-Parallel Circuit Difference:
The main difference between series and parallel circuits lies in how components are connected. In a series circuit, components are connected end-to-end, allowing the current to flow through them sequentially. In a parallel circuit, components are connected across each other, providing multiple paths for the current. Series-parallel circuits combine both configurations, offering a balance between sequential and parallel connections.
Series-Parallel Circuit Conclusion:
In conclusion, series-parallel circuits are a combination of series and parallel circuit arrangements. They offer flexibility and complexity in designing electrical systems. By understanding the formulas, laws, and differences between series and parallel circuits, engineers and technicians can analyze and design circuits more effectively.
How to Calculate Transistors in Parallel or Series?
Calculating transistors in parallel or series follows the same principles as calculating resistors in a series-parallel circuit. For transistors connected in series, the total current gain (hFE) is the product of individual current gains: hFE_total = hFE1 * hFE2 * hFE3 * ... For transistors connected in parallel, the total current gain is the sum of individual current gains: hFE_total = hFE1 + hFE2 + hFE3 + ...
To calculate the total resistance or current gain in a series-parallel circuit with transistors, apply the appropriate formulas based on the circuit configuration and the transistor specifications.
Conclusion:
Understanding series-parallel circuits is essential for designing and analyzing complex electrical systems. By knowing the formulas, laws, and differences between series and parallel circuits, engineers and technicians can effectively calculate and analyze the behavior of series-parallel circuits. Additionally, the principles used for calculating resistors in series-parallel circuits can be extended to calculate the total current gain in transistors connected in series or parallel.